Sign Up for a Circle Mint account Today
Start running your business with USDC. Get started with Circle Mint.
DeFi — which stands for decentralized finance — aims to replicate existing financial products and services using smart contracts and decentralized protocols on a blockchain.
In simple terms, DeFi refers to open-source financial software that operates independently on a blockchain network that anyone with an internet connection can use to access basic financial services — such as borrowing, lending, and investing — without the need for a financial intermediary.
For example, instead of depositing money in a savings account in a bank, a cryptocurrency holder could place funds into a decentralized lending protocol to earn interest — typically at a much higher rate than traditional savings accounts.
DeFi provides internet-native alternatives to popular financial services in the form of decentralized protocols on a blockchain. Essentially, what that means is that anyone with an internet connection can take part in the global financial system, even if they don’t have a bank account.
—Jeremy Allaire, Circle CEO
Individuals worldwide can use DeFi applications to earn interest, borrow funds, invest in new financial products, take out insurance policies, and more — all made possible by smart contracts and blockchain technology.
A smart contract is an irreversible, self-executing agreement that is written in computer code, and executed on an open-source, permissionless, decentralized blockchain.
Smart contracts are the heart of the decentralized finance movement because they allow DeFi protocols to function based on code and logic without the need for an intermediary or third party.
While Ethereum was the first smart contract blockchain, many others have risen to prominence including Algorand, Solana, Binance Smart Chain, Cosmos, and many others.
Technically, the age of decentralized finance started in 2009 with the birth of Bitcoin as it enabled individuals to store and transfer funds over the internet in a completely decentralized manner for the first time. However, what we refer to as DeFi today are decentralized, smart contract-powered applications on top of a blockchain that aim to replicate traditional financial services.
The first decentralized finance applications were decentralized exchanges (DEX) on the Ethereum network. A DEX leverages smart contracts to allow investors to convert ETH into ERC20 tokens, and vice versa.
The next step in the DeFi movement was the creation of yield-generation savings protocols in late 2018, with Compound Protocol as the frontrunner. In the following twelve months, numerous new lending and borrowing applications emerged as well as new types of decentralized financial applications.
The decentralized finance market has grown into a multi-billion dollar industry, with over $90 billion locked up in DeFi protocols as of January 10, 2022. According to DappRadar, there were over 655,000 daily unique active wallets across all chains in Q4 2021.
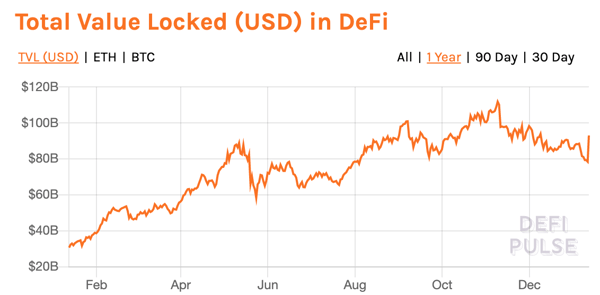
As the DeFi market continues to grow, new protocols are created to address new market needs as well as build innovative, new models for financial contracts.
The DeFi market is currently a playing field for experienced crypto investors who understand how to interact with smart contracts and manage multiple digital assets.
The average retail investor is yet to enter the DeFi market as the knowledge barriers are still quite high. In the future, we can expect that to change.
Tomorrow’s DeFi market will allow anyone across the globe to access a decentralized, global financial marketplace that provides all the services traditional financial institutions offer.
For example, a woman running a market stall in Kenya will be able to borrow funds at competitive rates from a decentralized lending protocol using just her smartphone.
Conversely, a merchant in India who is concerned about inflation could place funds into a yield-generating protocol that earns a higher APR than India’s prevailing inflation rate.
Some of the features that we expect to see in the future of DeFi are actually already possible thanks to market-leading applications such as Dharma, Aave, Compound, Yearn Finance, and more.
The DeFi movement is arguably one of the most promising markets in the financial technology sector, but that does not mean it is not without its challenges.
Currently, the vast majority of DeFi protocols operate on Ethereum. Unfortunately, the Ethereum ledger cannot handle the high number of transactions it is processing, as DApp usage exploded in 2020, mainly due to the boom in DeFi. As a result, transaction costs — known as “gas” fees — and transaction processing times have increased substantially on the Ethereum network, reaching the highest since 2017 this August.
For DeFi users, that means absolute returns are being diminished due to the high gas fees that need to be paid to move in and out of DeFi protocols. While the Ethereum developer community is working to address these issues with future network upgrades, the future of DeFi will likely be multi-chain.
Ethereum will not be the only blockchain network that houses DeFi protocols.
Second and third-generation layer 1 smart contract platforms like Algorand, Cardano, Solana, Binance Smart Chain, Cosmos, Polkadot, Luna, and Avalanche, are building rich, competitive DeFi marketplaces like Ethereum.
Global stablecoins will, therefore, also become multi-chain digital currencies. USDC is already taking that step by natively integrating with Algorand, Solana, Stellar, TRON, Hedera, and Avalanche blockchains with plans to expand to many more.
According to a 2021 Q1 report by crypto research firm Messari, "The stablecoin monetary base reached over $65 billion in Q1 and continues to rise at an accelerating pace. Stablecoins also facilitated a whopping $1 trillion in transaction volume, more than the previous four quarters combined. USDC was the biggest winner, growing its share by 17%.”
Dollar stablecoins, also known as dollar digital currencies, enable investors to generate yield on their crypto assets in the DeFi market while alleviating the potential adverse effects of market volatility.
If an investor places ETH into the Compound protocol to earn interest, for example, there is the possibility that an ETH price drop offsets all yield earned, leaving the investor with a loss. However, if the same investor uses a stablecoin, such as USDC, the value of the underlying asset would remain stable so the yield would remain unaffected by crypto market volatility.
Investors looking for more yield than traditional fixed-interest investments — such as savings accounts, money market funds, or bonds — can digitize their funds to earn above-average yields in the DeFi market. Arguably, the easiest and safest way to do that is to tokenize US dollars into USDC, which can then be used to deposit into DeFi protocols.
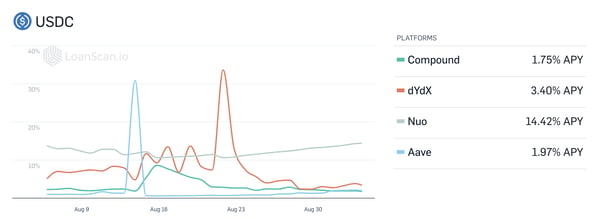
Unsurprisingly, digital dollar stablecoins are becoming increasingly important assets in the DeFi lending markets. USDC, for example, has established itself as one of the most popular lending assets on platforms such as Compound, dYdX, and Aave with lending rates ranging from 0.15% to 11.82% APY.
Start running your business with USDC. Get started with Circle Mint.
The vast majority of DeFi protocols operate on the Ethereum blockchain, the world’s leading smart contract platform. According to DeFi Prime, there are currently over 200 DeFi applications on Ethereum, ranging from decentralized exchanges and lending protocols to trustless derivatives trading platforms and yield-generating liquidity pools.
In the summer of 2020, Ethereum saw an eruption of decentralized finance protocols, which attracted massive amounts of attention and money. Before we dive into specific protocols, let’s quickly cover two aspects of DeFi that caused such a massive interest.
Arguably the most talked-about trend in today’s DeFi market is yield farming.
Yield farming refers to placing crypto assets into DeFi protocols to generate the highest returns possible.
Yield farming can take various forms, with the most common being depositing funds in high-yielding lending protocols. Compound and Dharma are two examples of the convergence of fintech and crypto, where crypto-native applications enable simple savings solutions.
The latest yield farming trend that emerged during "DeFi Summer" was the concept of liquidity mining.
Liquidity mining refers to providing liquidity to DeFi protocols such as decentralized exchanges in return for newly minted protocol tokens.
DeFi protocols Balancer and Compound, for example, reward liquidity providers with protocol-native tokens for participating on their platforms. As these tokens can be traded in the secondary market, an incentive structure is created where investors can earn substantial returns in the form of protocol tokens for contributing as much capital to a protocol as possible.
Now that we’ve covered a few key terms, let’s dive into some of the best DeFi protocols built on the Ethereum blockchain. In the next section we’ll cover the following groups of protocols:
If you bought cryptocurrency during the 2017 bull run markets, chances are you purchased it through a centralized exchange like Coinbase or Binance. As a response to this centralization, solidity developers (the programming language for building decentralized applications on Ethereum) created a decentralized exchange (DEX) using an Automated Market Maker (AMM) that deploys a Constant Product function (x*y = k), to allow anybody to buy or sell ERC-20 tokens against a liquidity pool.
DEXes are extremely popular. In fact, according to Messari’s Q1 2021 DeFi report, DEX volumes increased 236% since Q4 2020 to reach a total volume of over $217 billion.
With over $6 billion dollars in Total Value Locked (TVL) as of April 2021, Uniswap is the largest decentralized exchange. With the release of Uniswap v3, users can expect to take advantage of new features designed to lower costs and increase trading efficiencies.
Balancer is an autonomous market maker (AMM) protocol that rewards liquidity pool participants with its governance token, BAL, on top of pool fees. The more protocol participants contribute to a pool, the more they will earn in governance tokens, which is a prime example of liquidity mining.
Compound is an autonomous money market protocol that enables crypto investors to deposit digital assets to earn crypto-native interest. For example, Ethereum users can deposit USDC — which operates as an ERC-20 token — into the Compound protocol to earn an estimated 2.53% APY.
Conversely, an investor who wants to go long on margin could tap the Compound protocol to borrow USDC at 6.43% by providing collateral. The investor can borrow the funds for as long as his Borrow Balance does not exceed his Borrow Limit, at which point his position would be partially liquidated.
Another option for DeFi market participants is borrowing and lending two different stablecoins using the Compound protocol to earn as many COMP tokens as possible to generate a higher return than the interest rate differential between the borrowed and deposited funds. This would be another — albeit more esoteric — example of liquidity mining.
Getting a loan in the traditional financial system can be difficult and time consuming. In DeFi, getting a stablecoin loan only requires a few minutes and another digital asset to post as collateral.
In fact, it’s so simple that Messari’s crypto analysts reported lending deposits across all DeFi ecosystems reached $25 billion in Q1 of 2021, with Ethereum’s Compound capturing 53% of the market.
With over $7.4 billion in assets under management as of April 2021, Aave is one of the largest lending protocols in DeFi. With Aave, users can use a cryptocurrency like Bitcoin as collateral and receive a stablecoin loan or flash loan at attractive interest rates.
The loan amount is based on the riskiness of the underlying asset and its total value. This is known as a Loan-to-Value ratio. For example, a borrower can only borrow up to 70% of their Bitcoin’s value since it is a volatile asset, whereas borrowers can receive up to 80% of the value of their Ethereum.
On the other side of the lender-borrower equation, are individual or institutional liquidity providers who earn a percentage of the interest that is paid back by the borrower.
A yield aggregator finds the best yield farming opportunities across Ethereum’s entire DeFi ecosystem, and automatically moves your investment to the vehicles with the best returns.
Arguably one of the most innovative and prolific teams in all of DeFi, Yearn Finance, has built a suite of DeFi products including one of the leading yield aggregation products.
Yearn vaults optimize your investments returns by programmatically moving your capital into the best yield farming pools, and by sharing costs across all vault participants users save on gas fees, and earn passive income without needing to constantly follow the market.
While initially proposed over 30 years ago, the concept of perpetual futures was only actualized because of smart contract capabilities. Perpetual futures, or perps, are another 0-to-1 DeFi innovation.
Traditional futures contracts have an end date, and when the contract reaches maturity the investor needs to either buy or sell the underlying asset at the stated price.
With perpetual futures there is no expiration date which means investors are not obligated to buy or sell the underlying asset. Instead, they can trade the future contract indefinitely.
If you’re a betting person, prediction markets might be for you! Did you want to wager on the 2020 presidential election? How about if the Olympics will be canceled because of COVID-19? With prediction markets like Augur or Polymarket, this becomes possible.
Prediction markets work by giving bettors two options: for or against. While the result is undecided, the price for each side ranges between $0 to $1.00, and when we reach the end of the event being wagered on, the “for” token or the “against” token will reach $0 or $1.00.
For example, if you predicted that Tom Brady would win Super Bowl LV, your tokens would have been worth $1 once time ran out, and everyone who bet against Tom Brady would own tokens worth $0.
A synthetic asset is a digital asset that represents a real-world asset. By using a price oracle like Chainlink, a DeFi protocol like Synthetix can create a synthetic asset (like a stock), and keep the price equal to the real-world price of the underlying asset.
To do this, Synthetix creates a basket of stablecoins to represent the synthetic asset’s price, and then adds or removes stablecoins programmatically to manage the price.
In exchange for a monthly fee, individuals in traditional insurance markets receive coverage when they experience a claimable event like personal injury (health), accident (car), or theft (home).
DeFi insurance is like regular insurance, except DeFi insurance protocols like Nexus Mutual covers you against the loss of funds from events like bugs or exploits, and simultaneously rewards the community for assessing risks and claims.
For institutional investors looking to enter crypto capital markets they need to weigh risk and reward more carefully than retail investors. For this reason, tokenized risk protocols like Barn Bridge allow investors to sell risk and hedge against impermanent loss.
For example, if an adventurous FinTech company wanted to use a brand new DeFi protocol that was promising 30% returns on their USDC, and they needed to insure against losing their principal investment, they could use a peer-to-peer risk exchange like Saffron Finance to earn a lower return on their capital, say 20%, and be paid back by the risk takers if funds were lost due to a hack.
While decentralized lending and borrowing protocols have emerged and grown substantially, so have the more traditional centralized services built on top of crypto capital markets. Services like BlockFi and Coinbase have rolled out crypto-backed loans for both institutions and retail investors. According to CredMark, at the end of Q4 2020, there was $25.6B in crypto collateral on $13.3B of active debt — this is on top of what’s already locked up in DeFi.
Most centralized crypto services, meaning where the company custodies the private keys of its customers, will start to resemble crypto banks who offer a variety of financial services built on crypto, however, still with an intermediary providing services on top of decentralized protocols.
USDC is the fastest-growing, fully reserved digital dollar stablecoin that enables businesses and individuals across the globe to transfer digitized US dollars over the internet.
USDC is issued by regulated financial institutions and redeemable 1:1 for US dollars. All US dollar reserves are attested by global accounting firm, Grant Thornton LLP on a monthly basis to provide utmost trust and transparency.

USDC is a highly-transparent, regulated, price-stable digital currency that can be used to securely interact with DeFi protocols. Whether you are looking to borrow, lend, or take part in high yielding protocols, USDC offers a secure on-ramp for DeFi.
What’s more, experienced DeFi investors can use the Circle Mint as a home base to seamlessly tokenize US dollars and move digital dollars in and out of DeFi protocols, as well as back into fiat currency.
USDC possesses the largest stablecoin ecosystem in the world, with support from hundreds of applications, wallets, exchanges, payment services, OTC lending desks, and DeFi protocols.
Yield farming refers to placing crypto assets into DeFi protocols to generate the highest returns possible. For example, a person may deposit RAY-USDC into Raydium’s yield farm to earn interest in Raydium’s native token, RAY.